Science: The Environment:
A New Type of Small and High Performance Heat Sources for Environmental Solutions
By Dr. Keiji Taniguchi,
Fukui University; Dr. Tsugio Matsuura, Fukui Industrial Technology Center;
and
Dr. Sadakazu Watanabe, Fukui University
1.
Introduction
Environmental contamination generated by wastes has brought a number of serious
problems. Technically, there are two types of methods used for processing these
wastes: organic processing and heat processing. Particularly in the processing
of solid wastes, dioxins (poisonous material) generated by the low temperature
burning of solid wastes and medical wastes present a serious environmental
problem to nations throughout the world. In order to solve these problems, a
specially developed high temperature heat-source is required. We show here the
new structure of a simple and efficient arc-plasma heat source operated by the
multi-phase power source that is converted from commercial three-phase
alternating currents.
2.
Method
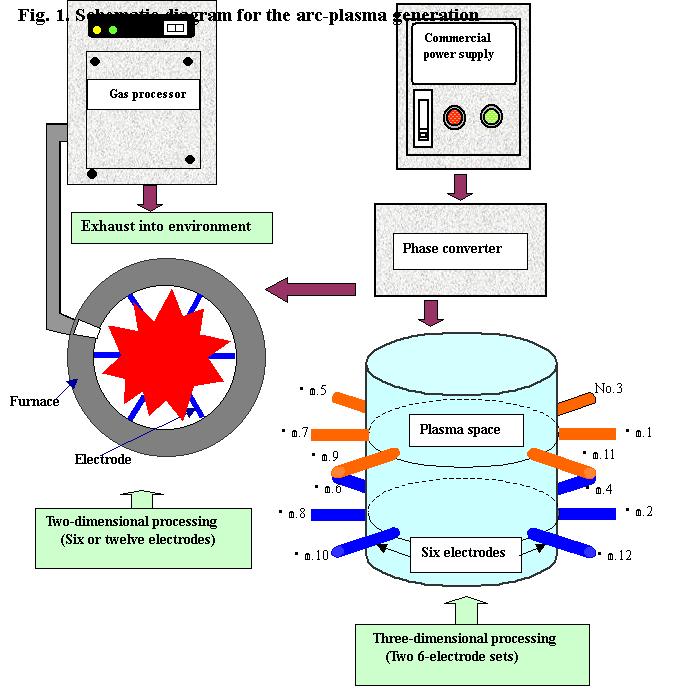
The
schematic diagram for the arc-plasma generation is illustrated in Fig. 1. The
power source of multi-phase alternating currents that is converted from the
three-phase commercial power supply is used for generating the arc-plasma. From
our target, using two sets of electrodes (each set consisting of six
electrodes) we can select either the two-dimensional arrangement constructed by
six or twelve electrodes, or the three-dimensional arrangement constructed by
both sets of electrodes as the operation mode of arc-plasma generation.
3. Estimation of minimum temperature
The energy radiated from the arc-plasma
is measured by using a spectrometer. Fig. 2 shows an example of the spectral
distribution which consists of two major parts: the black body radiation and
the line spectral radiation. From the peak value of the black body radiation,
we can estimate the minimum temperature value in the arc-plasma space. From
Fig. 2, the wavelength λm of the peak point is approximately 570 (nm). Therefore, the
temperature in the arc-plasma space is approximately 5000 (K) (this value was
calculated by the formula:![]() ). The effect for the line spectral radiation shown in Fig. 2
is not contained here at all. Therefore, this is the minimum value of
temperature.
). The effect for the line spectral radiation shown in Fig. 2
is not contained here at all. Therefore, this is the minimum value of
temperature.
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram for the arc-plasma generation
4. Examples of the processed results
The
first example is that of incinerated Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) and the
processed results are shown in Fig. 3(a) and Fig. 3(b), respectively. In
example 2, the medical waste material (used syringes) and the processed result
(melted needles and casings, which can then be recycled as raw material) are
also shown in Fig. 4(a) and Fig. 4(b), respectively.
5. Conclusion
This
method can easily obtain a significantly higher and wider temperature space as
compared with traditional methods. This method is particularly useful for
processing solid wastes which contain poisonous materials.
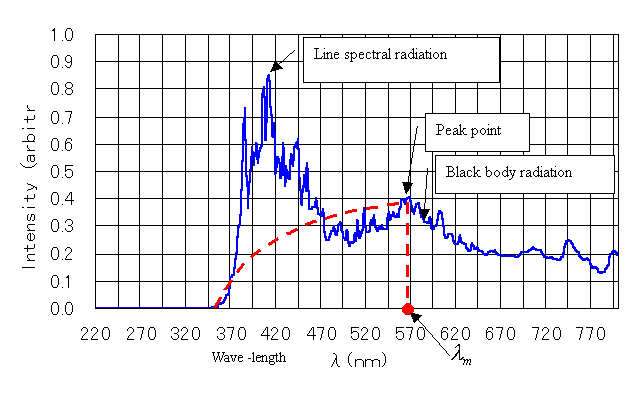
Fig. 2 Spectral distribution radiated from the arc-plasma
space
(This illustrates the case of employing six electrodes. Current is 200A/phase. Voltage between
phases is about 45(v))
Example
1: Municipal Solid Waste


Fig.
3(a) Incinerated MSW Fig.
3(b) Processed result
Example
2: Medical Waste


Fig.
4(a) Syringes Fig. 4(b)
Processed result
Dr.
Keiji Taniguchi is a member of the Editorial Advisory Board for Bibliotheque:
World Wide/BWW Publishers and the BWW Society; he is currently Honorary
Professor at Japan's Fukai University and at Xi'an University of Technology in
Xi'an China.
[ BWW Society Home Page ]
© 2002 The BWW Society/The Institute for the Advancement of Positive Global Solutions